Space Exploration
First Soft Landing on Moon
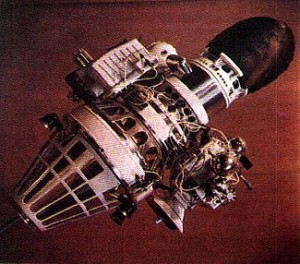
The unmanned Soviet Luna 9 spacecraft makes the first controlled rocket-assisted landing on the Moon. It was the first spacecraft to make a soft landing on any planetary body other than the Earth and to transmit photographic data to Earth. It was, however, the 12th attempt by the Soviets at a soft landing.
Space Shuttle Columbia Disaster

The Space Shuttle Columbia disintegrates during reentry into the Earth’s atmosphere, killing all seven astronauts aboard. The cause of the disaster was a piece of foam insulation the size of a small briefcase that broke off the external tank during launch and struck the leading edge of the left wing. This damaged the Shuttle’s thermal protection system (TPS), which protected it from heat generated by the atmosphere during re-entry. The damage allowed hot gases to penetrate and destroy the internal wing structure, resulting in the in-flight breakup of the Columbia.
The First American Satellite Launches Into Orbit

Explorer 1 is launched, which becomes the first American satellite to successfully make orbit.
First Ape into Space

50 years ago today, Ham the Chimp travels into outer space aboard Mercury-Redstone 2. Ham (whom was named this only after he survived the flight) was the first ape to fly into space. Note that apes include chimpanzees, gorillas, and humans, but NOT monkeys.
Phobos II Orbits Mars

The USSR’s Phobos II enters Martian orbit on its way to the moon Phobos. The spacecraft never completed its mission as it lost contact with mission control on March 27. Due to some unusual last photos received from Phobos II, speculation arose that it was destroyed by a UFO. Official reports blame the failure on the onboard computer. I wonder if mission control was trying to secure the Martian licensing rights to Tetris.
Space Shuttle Challenger Disaster

On this cold January morning, the Space Shuttle Challenger broke apart after liftoff, killing all seven astronauts on board. Contrary to popular belief, while the external fuel tank did combust, the Challenger didn’t truly explode as much as it was torn apart by aerodynamic forces.
Apollo 1 Tragedy

Astronauts Gus Grissom, Edward White and Roger Chaffee are killed in a fire during a test of their spacecraft at the Kennedy Space Center. After the fire, the spacecraft and planned launch which never took place was posthumously named Apollo 1, in the astronauts honor.
Ranger 3 Launched

Ranger 3 is launched to study the Moon. The space probe was designed to transmit pictures of the lunar surface to Earth stations during a period of 10 minutes of flight prior to impacting on the Moon. Due to a series of malfunctions, the spacecraft missed the Moon by 22,000 miles.
Opportunity Lands on Mars

Opportunity rover (MER-B) lands on surface of Mars, three weeks after its twin, Spirit (MER-A), touched down on the other side of the planet.
First Fly-By of Uranus

The interplanetary probe Voyager 2 makes the first fly-by of the planet Uranus. During its study of Uranus, it finds 10 previously undiscovered moons.
Voyager 2 still is transmitting data to this day, and a Twitter feed reports on its progress.