Miscellaneous Technology
Sirius and XM Merger Approved
First Ford Model A Sold

Ford sells its first Model A car to Ernst Pfenning of Chicago, Illinois. This was Henry Ford’s 3rd attempt at creating a company that manufactured cars, incorporating just over a month earlier. The initial $28,000 investment was down to $300 before this first Model A was sold. However, it was the Model T that solidified Ford’s standing in automotive history.
A Whole New Way to Drive a Screw

Several US patents are issued for the Phillips-head screw and screwdriver to inventor Henry F. Phillips. Phillips founded the Phillips Screw Company to license his patents. One of the first customers was General Motors for its Cadillac assembly-lines. By 1940, 85% of U.S. screw manufacturers had a license for the design.
The First 16mm Film System Introduced
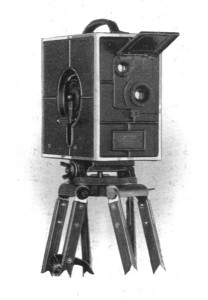
Kodak introduces the hand-cranked Cine-Kodak Model A, the first complete 16mm film system. 16mm film was developed to be an amateur alternative to 35mm film most often used by professionals. However, it found widespread use during World War II and later for television production, especially TV news. 16mm film is still in use today for certain applications.
Sony Walkman Makes Music Portable

The first Sony Walkman, the TPS-L2, goes on sale in Japan. It would go on sale in the US about a year later. By allowing owners to carry their personal music with them, the Walkman and their iconic headphones introduce a revolution in listening habits and popular culture at large.
The Transition to Transistors Begins

Originally designed to create improvements to electromechanical relays and vacuum tubes in telephone switching equipment, Bell Labs holds a press conference in New York to publicly demonstrate the first point-contact transistor. The transistor represents a significant advance in technology. As it is developed over the next few years, it will become the successor to the vacuum tube, the primary method of controlling electronic circuitry at the time. The use of transistors allows the development of the integrated circuit and microchips which kickstarted the rapid advance of electronic and computerized technology over the last 70+ years. Every industry that utilizes technology, from communications to computers to space travel to video games to media, owes a great deal to the development of the transistor.
I PC, UPC …
 June 26, 1974
June 26, 1974
A Universal Product Code (UPC) is used to ring up a purchase for the first time at a Marsh Supermarket in Troy, Ohio. The first item scanned was a 10-pack of Juicy Fruit gum. Take that to your trivia contents!
The First Practical Typewriter Patented
 June 23, 1868
June 23, 1868
Latham Sholes, Carlos Glidden, and Samuel Soule are awarded a patent for the “Type-Writer” which would become the basis for the first practical and commercially successful typewriter. Evolving into what would become known as the Sholes and Glidden typewriter (which would later become the Remington No. 1), one of its lasting legacies was the introduction of the QWERTY keyboard, which is still the most popular keyboard layout in the world to this day.
A popular theory states that the design of the QWERTY keyboard was intended to slow down typists in order to minimize the clashing of the typebars which would jam up the early typewriters. There is little evidence to support this theory, however, and a research study published in 2011 asserts that the QWERTY design was more directly influenced by feedback from telegraph operators who were early adopters of typewriters and found previous keyboard layouts inefficient.
Greenwich Becomes Mean
June 22, 1675

UNIX and UNIX-based operating systems keep time by using UTC and applying an offset for the local time zone. Notably only the Windows operating system uses local time as the assumptive basis for your computer’s clock. In fact, UNIX-based operating systems define the current time by the number of seconds which have passed since 00:00:00 UTC on Thursday, 1 January 1970, otherwise known as the UNIX epoch. So for those of you following along, a decree by a king in 1675 is the basis for how much of our technology of today keeps track of time.
Ford Motor Company Incorporated

Henry Ford incorporates the Ford Motor Company with ten investors and $28,000. Ford will begin building automobiles on Mack Avenue in Detroit in a converted factory that previously produced wagons. This was Ford’s 3rd attempt at building a company that produced cars and the investment was down to $300 before the first Ford was sold. Eventually the Ford Model T would be largely responsible for popularizing the automobile to the general public, at one point representing half of all cars on the road.
 July 25, 2008
July 25, 2008