Miscellaneous Technology
Photocopying Invented
In a makeshift lab on the second floor of a rental house, Chester Carlson and his assistant Otto Kornei successfully invent the process that would lead to the photocopier. Carlson had written “10.-22.-38 ASTORIA” on a piece of paper and these became the historic words that were the first photocopied. Ironically, Kornei had so little faith in the invention that within a year he quit working for Carlson and willingly gave up any claims he had on the process. However, Carlson would later gift Kornei 100 shares of the Xerox corporation that would eventually be worth $1 million.
Edison Perfects Light Bulb
Thomas Edison perfects the first commercially practical incandescent light bulb. Using a filament of carbonized cotton thread, his first attempt at this design results in a bulb that lasts about 13.5 hours before burning out. He later extends the life of the bulb to 40 hours. Edison’s successful design came only after he had tested over 6,000 different vegetable fibers during a span of over 18 months running 1,200 experiments and spending $40,000.
Triode Announced
Dr. Lee DeForest announces his three-element electrical vacuum tube, later known as a triode. The triode was able to produce a large voltage-amplifying effect, which when used to amplify weak signals, will make long-distance communication possible for the first time.
Edison Electric Light Company Formed
Thomas Edison and a group of investors form the Edison Electric Light Company. The goal of the company was to provide financial support for Edison’s electric light experiments and work on developing an electrical lighting system for an entire city. The long-lasting carbonized filament light bulb was developed by Edison while working for this company. Eventually this and several other Edison companies were merged to form General Electric.
Comptometer Patented
Dorr E. Felt is granted the second of two patents on his comptometer, the first practical and commercially successful key-driven mechanical calculator. Various comptometers were in continuous production from 1887 to the mid 1970’s.
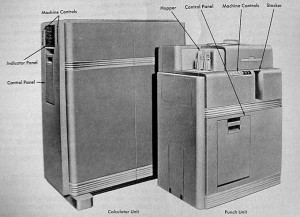
The First Transistor Calculator
IBM researchers modify an existing model 604 vacuum tube calculator to use transistors. This experiment didn’t shrink the desk-sized machine nor make it any faster, but it did use only 5% of the power the vacuum tube-based design did. Encouraged by this successful experiment, IBM introduced the first commercial transistor calculator 4 years later, the model 608.
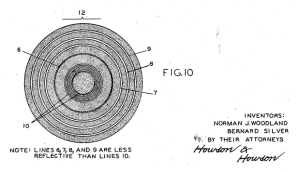
Barcode Technology Patented
American inventors Norman Joseph Woodland and Bernard Silver are granted US Patent #2,612,994 for “Classifying Apparatus and Method,” described as “article classification through the medium of identifying patterns.” Of course, today we better know these “identifying patterns” as barcodes. Woodland and Silver eventually sold their patent for only $15,000 but were later inducted into the Inventors Hall of Fame.
Barcodes were first used commercially in 1966 and it rapidly developed that eventually by 1970, there was a requirement to have some sort of industry standard set. A company called Logicon Inc. created the Universal Grocery Products Identification Code or UGPIC for short in order to implement the barcode throughout the retail industry.
Monarch Marking, based in the United States of America, was the first company to produce barcode equipment using UGPIC for retail trade use. British company, Plessey Telecommunications followed suit, creating their equipment later in the same year.
The UGPIC was transformed into UPC, or Universal Product Code symbol set, which is still used in the United States of America. The first piece of equipment using UPC was installed in a Marsh’s supermarket in Ohio and the first product checked out using a barcode was a packet of Wrigley’s Juicy Fruit Chewing Gum on June 26, 1974.
Special thanks to Jonny Rowntree of Elanders UK for sending me the background information for this article!
Photocopying Patented
Chester Carlson is issued a patent on a process called electrophotography, now commonly known as photocopying. It was not until 1946 that a company had any interest in pursuing photocopying commercially. The Haloid Company finally licensed Carlson’s patent and created the word xerography to differentiate the process from traditional photography. Eventually, photocopying became such a large part of the company’s revenue that Haloid changed their name to Xerox.
Transistor Patented
AT&T Bell Laboratories researchers John Bardeen, Walter Brattain, and William Shockley receive a US Patent for their invention of the transistor, which they had successfully demonstrated two years earlier. The transistor completely revolutionized the development of electronic and computerized technology.