The Internet
The First Mass Unsolicited Commercial E-mail, i.e. Spam
Gary Thuerk, a marketing representative for Digital Equipment Corporation, sends out an e-mail promoting an open house for the company’s latest computer systems to 393 recipients on the ARPANET, a precursor to the modern Internet. While this number sounds small by today’s standards, this was all the ARPANET users on the west coast of the United States. Given that this was an unsolicited commercial e-mail, it is now considered the first of its kind. In other words, the first spam message well before the term was coined. It brought a quick and negative response from many users and Thuerk was warned by ARPANET administrators that mass mailings were not an acceptable use of the network. The backlash notwithstanding, the open house was largely successful with over $12 million dollars of DEC equipment being sold. I guess it was better to ask forgiveness than permission in this case!
World Wide Web Made Public Domain
At the urging of Tim Berners-Lee, the creator of the World Wide Web protocol, the directors of CERN release the source code of World Wide Web into the public domain, making it freely available to anyone, without licensing fees. The decision to make the World Wide Web software and protocols freely available is considered by some as possibly the single most important moment in the history of the Internet. In fact, some historians mark this as the birth of the Web.
Sprechen Sie Sassy?
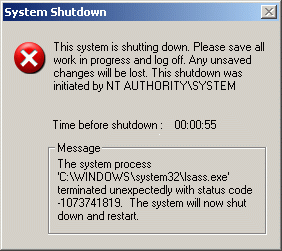
The Sasser worm is released into the wild, infecting over 1 million Windows XP and Windows 2000 computers worldwide. Although the worm did not have an intentionally destructive payload, it caused many computers to slow down or crash and reboot repeatedly along with clogging up network traffic. Among the effects of the worm, the British coast guard had to resort to paper maps for the day, a French news agency lost satellite communication for hours, Delta Airlines had to delay or cancel many flights, and the University of Missouri had to disconnect its network from the Internet. Looks like 1 million PC users stepped in a big pile of sassy!
Ironically it has been speculated that the author of Sasser, a German computer science student Sven Jaschan, reverse engineered Microsoft’s patch for the LSASS vulnerability that was released earlier in the month in order to create the worm. Knowing that most computers would not have been patched and that it would spread quickly, he released the worm on this day, his 18th birthday. Lucky for him the German government determined that he had actually written the worm while he was 17, so while he was found guilty of computer sabotage, he was tried as a minor and given a 21 month suspended sentence. He now works as a security expert and consultant. Now that’s Sassy!
iTunes Music Store Launched; Record Execs Wet Themselves

Apple Computer launches the iTunes Music Store. The store sells music for 99¢ a song for use with the Apple iPod and iTunes software. It is not the first service to sell digital music, but it will become the first to gain widespread popularity. The service will be an instant success, selling over one million songs in its first week and going on to change the music industry forever. The iTunes Music Store is now the #1 music retailer in the United States, surpassing Wal-Mart in 2008.
Do You Yahoo?

Yahoo! begins advertising its web-based search service on national television, featuring the tag line “Do You Yahoo?”. The ads first air during Late Night with David Letterman, Saturday Night Live, and Star Trek. This was a very early example of the Internet entering into the mainstream.
First YouTube Video

The first video uploaded to YouTube, “Me at the zoo,” is posted on April 23, 2005 at 8:27 PM by co-founder Jawed Karim. For now being a piece of history, the video is actually pretty dumb.
Note to future entrepreneurs: what you do may be for posterity. Choose wisely.
Mosaic 1.0

Version 1.0 of the web browser Mosaic is released by the National Center for Supercomputing Applications. It’s the first software to provide a graphical user interface for the emerging World Wide Web, including the ability to display inline graphics. The lead Mosaic developer is Marc Andreesen, one of the future founders of Netscape.
My first experience with the World Wide Web was in 1993 using Mosaic on a Mac in my dorm’s computer lab. I had no idea what I had discovered until a few months later.
Metallica Loses Their Cool

The heavy metal group Metallica sues Napster, alleging copyright infringement and racketeering. This lawsuit, later joined by Dr. Dre, as well as other lawsuits from the RIAA, eventually caused the original Napster service to shut down and file bankruptcy. However, the Pandora’s Box that Napster opened could not be closed and digital distribution changed the music industry forever.
As for Metallica, their reputation was tarnished for some time by this move. Ironically, Metallica owed much of their early popularity to the spread of unauthorized copies of their early albums. As the heavy metal genre in general and Metallica in particular did not get much airplay at that time, it was reported that Metallica quietly encouraged the free spread of their music in the early 80’s. Therefore many viewed Metallica’s action against Napster as hypocritical and greedy.
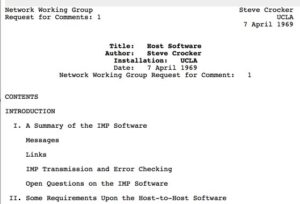
RFC 1 Defines the Building Block of Internet Communication
Steve Crocker, a graduate student at UCLA and part of the team developing ARPANET, writes the first “Request for Comments“. The ARPANET, a research project of the Department of Defense’s Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA), was the foundation of today’s modern Internet. RFC 1 defined the design of the host software for communication between ARPANET nodes. This host software would be run on Interface Message Processors or IMPs, which were the precursor to Internet routers. The “host software” defined in RFC 1 would later be known as the Network Control Protocol or NCP, which itself was the forerunner to the modern TCP/IP protocol the Internet runs on today.
There is a very interesting history to how RFCs came about, itself fittingly documented in RFC 1000. Long story short, the initial design of the ARPANET was not well defined. The students and researchers on the ARPANET team were expecting professionals from the government to come in and define their objectives more clearly. As it started to become evident that there was no specific design forthcoming and possibilities were being discussed informally, the working group decided that they should start writing down and organizing their ideas. However, they were also concerned that by formally documenting their concepts that it might seem like they were taking authority and would possibly offend some hypothetical “official protocol designers” from the government. Therefore Steve Crocker chose to carefully title the document “Request for Comments” so that the point was made that these were not official publications and that in fact, they were asking for others working on the project to add their input. As more RFC documents were written describing and defining the earliest building blocks of the ARPANET, these became the unofficial method of documentation and discussion within the ARPANET Networking Working Group (itself loosely defined in RFC 3). This laid the foundation for the eventual Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) which today establishes many official Internet Standards. Today RFCs are the official publication of the IETF where Internet developments are proposed and official Internet Standards are defined. As of early 2023 there have been nearly 9500 RFCs published.
Could it be … SATAN?

Dan Farmer and Wietse Venema release to the Internet the Security Administrator Tool for Analyzing Networks, known by its acronym, SATAN. SATAN is a network scanner for investigating the vulnerability of remote systems. Designed for use by network administrators, the program will soon generate controversy over the ethics of freely releasing powerful security tools to the general public. And it didn’t please the Church Lady one bit, either.