Space Exploration
Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter Reaches Red Planet
The Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) arrives at the Red Planet and enters its initial orbit. The MRO’s primary mission was to search for the existence of water on Mars along with several other objectives. Initially designed to carry out its main mission for two years and supporting objectives for four years, the MRO is still in operation as of 2023. The MRO has returned over 445 terabits of data, helped locate safe landing sites for NASA’s Mars landers and discovered ice and possible flowing water on the Red Planet’s surface.
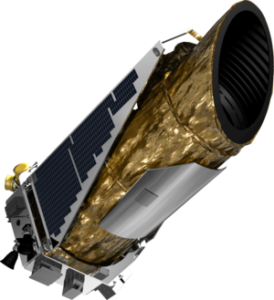
NASA Launches Kepler
Kepler, the first planet seeking space telescope is launched by NASA on a Delta II rocket from Cape Canaveral. While intended for a three-and-a-half year mission, Kepler stayed operational for 9 years until it ran out of fuel in 2018. Kepler discovered more than 2,600 planets outside our solar system.
Pioneer 10 Launched

NASA launches Pioneer 10 spacecraft on a mission to explore the outer planets of the solar system. It will pass near Jupiter and Neptune before leaving the solar system.
First Spacecraft to Land On Another Planet
First Saturn 1B Rocket Launch

The first Saturn 1B rocket is launched from Cape Canaveral. The Saturn 1B was primarily used for testing the Apollo spacecraft while the larger Saturn V rocket that was necessary for travel to the Moon was being developed. Later, after completion of the Moon landing program, The Saturn 1B was used for manned Skylab flights and the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project. In total, the Saturn 1B was launched 9 times with no failures.
Final Mission of Space Shuttle Discovery

February 24, 2011
The Space Shuttle Discovery launches on flight STS-133, its 39th and final mission, transporting several items to the International Space Station, including a humanoid robot called Robonaut2, nicknamed R2. Discovery was the longest-serving orbiter, flying more missions than any other Space Shuttle.
“First” US Rocket to Reach Outer Space

Considered the first US rocket to reach outer space by NASA, Bumper 5 is launched from the White Sands Proving Grounds in New Mexico. The rocket was a combination of a modified captured German V-2 ballistic missile with a US-designed WAC Corporal rocket. It reached a record altitude at the time of 244 miles. The later named and established Kármán line, which is 62.1 miles (100 kilometers) above the Earth’s sea level, is considered the upper limit of Earth’s atmosphere and the beginning of Outer Space.
Interestingly, according to information found online there were other previous captured V-2 test flights launched from White Sands that reached higher than 100 km prior to Bumper 5. Still, the significance of Bumper 5 was that it was the first successful two-stage rocket launch, which proved the feasibility of the basic design of staged rockets that made successful space flight a reality.
Space Station Mir is Launched

The Soviet Union launches the core module of the Mir space station. The core module will provide living quarters for the cosmonauts, including a galley, cooking elements, storage, individual crew cabins and personal hygiene area. Five additional modules will be launched between March 1987 and April 1996.
John Glen Becomes First American to Orbit Earth

John Glenn becomes the first American to orbit the Earth, riding aboard Friendship 7. Glenn orbits the Earth three times in four hours, fifty-five minutes. NASA accomplishes the landmark using an IBM 7030 Stretch supercomputer.
First Flight of Space Shuttle – Just Not Into Space

The first Space Shuttle orbiter, the Enterprise, embarks on its maiden flight in “captive mode,” attached to the top of a Boeing 747 jumbo jet. The flight is the first of five captive flights before the orbiter is finally released to land on its own. The nine month test program is conducted through November 1977 at the Dryden Flight Research Facility to demonstrate that the orbiter can fly and land like an airplane. The Enterprise, while the first shuttle to fly, was not the first space-worthy orbiter and was only used for testing purposes.

 March 1, 1966
March 1, 1966