Archive for February 2024
RADAR Demonstrated for First Time
Scottish physicist Robert Watson-Watt, considered by many to be the inventor of RADAR (RAdio Detection And Ranging), first demonstrates its feasibility. Watson-Watt had been experimenting using radio waves to locate thunderstorms and thought of the idea of using it to detect aircraft. The use of RADAR is widely considered one of the key factors for the Allied victory in World War II. The research that went into further improving RADAR branched off into many areas including the invention of the transistor, which of course, allowed the development of many modern computerized technologies.
Apple Sells 10 Billionth Song

Apple announces that its has sold its ten billionth song through its iTunes Store. The ten billionth song, “Guess Things Happen That Way” by Johnny Cash, was purchased by Louie Sulcer of Woodstock, Georgia, whom Apple awarded a US$10,000 iTunes Gift Card. It took Apple over five years to sell its first five billion songs but only a year and a half to sell its second five billion songs.
First Check Photographing Device Patented

The first bank check photographing device patent is issued in the US to its inventor, George McCarthy, who called it the Checkograph. The machine photographed checks onto 16mm motion picture film using a conveyor belt. The Kodak company bought this invention in 1928 and marketed it under its Recordak division.
Electric Motor Patented

With his wife Emily, and a colleague Orange Smalley, Thomas Davenport received the first American patent on an electric motor in 1837, U. S. Patent No. 132.
Final Mission of Space Shuttle Discovery

February 24, 2011
The Space Shuttle Discovery launches on flight STS-133, its 39th and final mission, transporting several items to the International Space Station, including a humanoid robot called Robonaut2, nicknamed R2. Discovery was the longest-serving orbiter, flying more missions than any other Space Shuttle.
First Phone and TV Satellite Relays

The first satellite telephone and television relays are established through the communications satellite Echo 1. The satellite was basically a big metallic balloon that simply bounced microwaves off its surface. Simple, but effective.
“First” US Rocket to Reach Outer Space

Considered the first US rocket to reach outer space by NASA, Bumper 5 is launched from the White Sands Proving Grounds in New Mexico. The rocket was a combination of a modified captured German V-2 ballistic missile with a US-designed WAC Corporal rocket. It reached a record altitude at the time of 244 miles. The later named and established Kármán line, which is 62.1 miles (100 kilometers) above the Earth’s sea level, is considered the upper limit of Earth’s atmosphere and the beginning of Outer Space.
Interestingly, according to information found online there were other previous captured V-2 test flights launched from White Sands that reached higher than 100 km prior to Bumper 5. Still, the significance of Bumper 5 was that it was the first successful two-stage rocket launch, which proved the feasibility of the basic design of staged rockets that made successful space flight a reality.
First Mobile Phone Virus
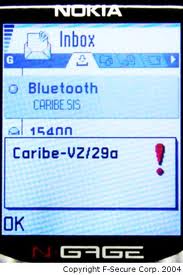
The discovery of the first mobile phone virus, Cabir, is accounced. Specifically, Cabir is a worm which infects phones running the Symbian OS. Whenever an infected phone is activated, the message “Caribe” is displayed. Infected phones also attempts to spread the virus through Bluetooth signals.
Radio Gets Controlled

The Radio Act of 1927 is signed into law. The Act creates the Federal Radio Commission (FRC), which will later be replaced by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC). Ironically, the act claims to recognize broadcasters’ right to free speech yet the Federal Radio Commission solely controls allocation of licensing, frequencies, transmitter power, and broadcasting hours. Doesn’t exactly sound like free speech to me, but hey I’m sort of prickly like that.
Holy Type!

While maybe not exactly accurate, February 23rd, 1455 is generally accepted as the date that the Gutenberg Bible was first published. This was the first book on record to be printed on movable type. Until that point, books were copied by hand, which was obviously a slow, laborious process.
On a side note, I challenge anyone to come up with a historical date in technology earlier than this one! Good luck!