The Internet
Pets.com Put to Sleep
After only 2 years in business, Pets.com shuts down operations. Cited as one of the biggest failures of the dot-com bubble, Pets.com was able to gain significant brand recognition through its extensive marketing campaign and sock puppet mascot, but lost money due to an unsustainable business plan. Ironically, the company’s best selling product was its sock puppet. And yes, I own one.
Morris Worm Tunnels Through Internet
Robert Morris of Cornell University launches a self-replicating worm as part of a research project designed to determine the size of the early Internet. It was intended to count the number of computers that initiated connections when the worm was loaded onto them. However, due to a programming error, the “Morris Worm” began repeatedly infecting machines, clogging network traffic and causing machines to crash. Eventually the worm spread to 6,000 machines, which was roughly 10 percent of the Internet at the time, causing significant downtime for government and university systems for two days. Morris was dismissed from Cornell, sentenced to three years probation and a $10,000 fine.
First Message on the Internet
October 29, 1969
UCLA student Charley Kline attempts to transmit the text “login” to a computer at the Stanford Research Institute over the first link on the ARPANET, which was the precursor to the modern Internet. After the letters “l” and “o” are sent the system crashed, making the first message ever sent on the Internet “lo”. About an hour later, after recovering from the crash, the full text of “login” is successfully sent.
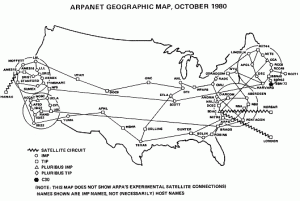
First Major ARPANET Outage
October 27, 1980
The ARPANET, the precursor to the modern Internet, stops functioning for about four hours after the network’s routing tables are corrupted by a malfunctioning Interface Message Processor (IMP).
IMDb Launched
Colin Needham, an English movie fan, launches the “rec.arts.movies movie database”, which would later be known as the Internet Movie Database, or IMDb. An engineer working for HP at the time, by 1996 Needham quit his job to work on IMDb full-time. The IMDb is one of the most visited sites on the Internet and was acquired by Amazon in 1998. Needham is still the General Manager of the IMDb to this day.
Google’s Fake Birthday
September 27th, 1998

Turn That Frown … Sideways
September 19, 1982
In a posting made to a Carnegie Mellon bulletin board, Professor Scott Fahlman proposes the first known use of emoticons (also known as smilicons or smileys). While the use of emoticons became widespread during the 80’s and 90’s, their origin remained unknown until September 10, 2002, when the original message was retrieved from backup tape.
The following is the original message:
19-Sep-82 11:44 Scott E Fahlman :-) From: Scott E Fahlman <Fahlman at Cmu-20c> I propose that the following character sequence for joke markers: :-) Read it sideways. Actually, it is probably more economical to mark things that are NOT jokes, given current trends. For this, use :-(
Side note, personally I may have been the first to use a smilicon in printed form when I put one in my high school yearbook with my senior quote under my picture. Edwardsville High School Class of 1992!
The First Internet Search Engine
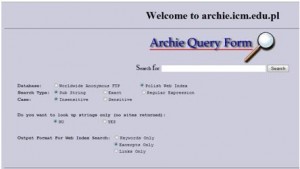
The first Internet search engine, Archie, is launched. It was used to index FTP archives to make finding files easier. However, as the technology for the World Wide Web was not invented until later in the year, it was not the first web search engine.
RIAA Sues A Twelve-Year Old

The Recording Industry Association of America (RIAA) sues 261 people for sharing music on Internet peer-to-peer networks, including 12-year old Brianna LaHara. Eventually bringing suit against at least 30,000 people, the RIAA intended to reduce the amount of music being shared, but instead generated a public backlash against the established recording industry.
“Google Satellite” GeoEye-1 Launched

After 5 months of delays, the high resolution earth observation satellite, GeoEye-1, is launched from Vandenburg Air Force Base. Owned by the corporation GeoEye, Inc., GeoEye-1 is capable of taking high resolution images with detail of down to 16 inches. However, the US Government has restricted that resolution for its own use. Commercial usage is limited to resolutions with detail down to 20 inches. As the exclusive licensee of the images for online mapping purposes, Google had its logo on the Delta II rocket that was used to launch GeoEye-1.