Computers
Dell Founded

Dell Computer Corporation is founded by Michael Dell, running the direct-to-order PC company from his dorm room. Using this innovative direct-to-order model, Dell, Inc. eventually became the largest manufacturer of PCs in the world for many years. Through ups and downs, it is still currently in the top 3 as of 2022 in market share for personal computers.
Microsoft Acts Mousey

Microsoft introduces the Microsoft Mouse for IBM and IBM-compatible PCs. The mouse featured two green buttons and is available by itself or will later be bundled with the new Microsoft Word software, which Microsoft would release in September. Because of the green buttons, the mouse was nicknamed the “Green-Eyed Mouse”, which may have been a fitting name given it’s similarity to the Shakesperian phrase “green-eyed monster” to describe jealously. It was no secret Bill Gates was very envious of what Apple was creating with the Lisa and later Macintosh computers and their mouse-driven interfaces. Microsoft will manufacture nearly one hundred thousand units of their first mouse, but will only sell five thousand before introducing a second, more popular version in 1985.
Microsoft would go on to create a very successful line of mice and other computing peripherals over the years, but almost ironically Microsoft announced in April of 2023, nearly 40 years later, that they would end the production of Microsoft-branded peripherals and focus on their Surface-branded peripherals. This came months after Microsoft announced a 30% year-over-year drop in revenue from devices, cut 10,000 jobs, and announced “changes to their hardware portfolio”.
Commercial Computer Mouse Introduced

Xerox introduces the Xerox 8010 Star Information System, the first commercial system utilizing a computer mouse, among other now commonplace technologies. The 8010 was geared towards business and was not a commercial success, therefore the mouse remained in relative obscurity until the Apple Lisa, but more prominently the Apple Macintosh, brought the mouse into the mainstream.
Chernobyl Virus Melts Down PCs
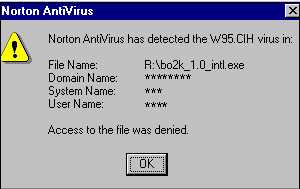
The first known virus to target the flash BIOS of a PC, the CIH/Chernobyl Virus triggers its payload on this day, erasing hard drives and disabling PCs primarily in Asia and Europe. One of the most destructive viruses in history, it is estimated that 60 billion PCs were infected worldwide causing $1 Billion in damages.
The virus had been created exactly one year earlier on April 26, 1998 by Taiwanese student Chen Ing-hau and set to trigger its destructive payload exactly one year later. It began to spread in the wild and was first discovered in June of 1998, given the name CIH due to the author’s initials discovered in the virus code. From this time forward it was reported that a variety of companies accidentally distributed the virus through various downloads, updates, and CDs. When the virus triggered on this date it just happened to coincide with the date of the Chernobyl disaster in 1986 and therefore the press began to call it the Chernobyl virus, even though there has never been any evidence to show that this date was chosen intentionally for this reason.
IBM Licenses PC Patents
The Tandy Corporation holds a press conference to announce plans to build clones of IBM’s PS/2 system computers. The conference comes soon after IBM’s announcement that it would license patents on key PC technologies. IBM made this decision as they realized they were losing control of the “IBM-compatible” PC market and could make more money licensing the technologies. Within five years, IBM clones will become more popular than the original IBM machines themselves. Eventually IBM would leave the PC manufacturing business altogether, selling their PC division to Lenovo in 2005.
Moore’s Law Published
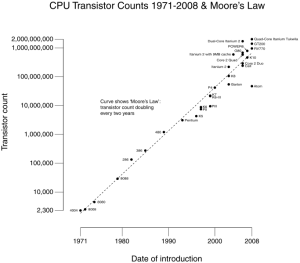
Electronics magazine publishes an article by Gordon Moore, head of research and development for Fairchild Semiconductor and future co-founder of Intel, on the future of semiconductor components. In the article, Moore predicts that transistor density on integrated circuits will double every eighteen months for “at least” the next ten years. This theory will eventually come to be known as Moore’s Law and has largely held true to this day. Controversy exists over whether Moore’s Law remains applicable, however time will tell just how long Moore’s Law will continue to remain true.
First Megabit Chip in Commercial Product
Newspapers report that IBM’s Model 3090 mainframe has become the first commercial computer to use a megabit memory chip, 4 times the storage capacity of the then current generation of 256 kilobit chips. To give context to that amount of storage, it was reported that a megabit chip could store over 1 million bits of data, which translated to about about 100 double-spaced typewritten pages. At the time most personal computers were still using 64 kilobit memory chips.

Osborne Executive Introduced

The Osborne Computer Corporation officially announced the Osborne Executive portable computer, the follow-up to its extremely successful Osborne 1. This is the computer that according to lore, took down the company. Known as the Osborne Effect, the legend is that by leaking the announcement of this computer earlier in the year, dealers cancelled all orders for the Osborne 1, effectively destroying the company’s cashflow and hindering operations going forward. This resulted in the cancellation of the company’s IPO and eventually to bankruptcy.
The reality may not be so simple, but my research shows that the Osborne Effect may have been a contributing cause to the company’s demise, along with the rise of competitors, the introduction of the IBM PC, and mismanagement by the company’s president, brought in by investors to provide “adult supervision”.
Apple and Commodore

On the same day at the first annual West Coast Computer Faire, both the Apple II and Commodore PET 2001 personal computers are introduced. Ironically, Commodore had previously rejected purchasing the Apple II from Steve Jobs and Steve Wozniak, deciding to build their own computers. Both computers used the same processor, the MOS 6502, but the companies had two different design strategies and it showed on this day. Apple wanted to build computers with more features at a higher price point. Commodore wanted to sell less feature-filled computers at a lower price point. The Apple II had color, graphics, and sound selling for $1298. The Commodore PET only had a monochrome display and was priced at $795.
Note, it was very difficult finding a picture with both an original Apple II (not IIe) and Commodore PET 2001. I could only find this picture that also includes the TRS-80, another PC introduced later in 1977.
PC Industry Born

The first annual West Coast Computer Faire is held over three days in San Francisco, California, attended by 12,750 people. The Faire features the debut of the Apple II computer, which features 16KB of memory, BASIC, a built-in keyboard, eight expansion slots, and built-in high-resolution color graphics. Many credit this event and the launch of the Apple II as giving birth to the personal computer industry.